Large page sizes can affect SEO and performance and cause search engines to rank your website lower. As such, now is the time to start understanding page size because, in the digital world, it matters. So, if you’re looking to improve your website performance, this post is for you.
Essentially, the “heavier†your page size is, the slower it’ll take to fully load and be ready to be consumed by site visitors. When your web page has a slow response time, it ultimately affects the overall website performance and user experience – two of the most important SEO factors.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into what page size is and the factors that affect it. We’ll also talk about what role it plays in your overall SEO strategy. By the end of this, you’ll know methods you can apply to your website to ensure it’s not dragged down the rankings and keep your best chances of ranking on top.
What Is Page Size And What Contributes To It?
A web page’s size is a measure of how much data it contains. It’s the total amount of data that is sent from the server to the browser when a visitor requests a page. This includes all elements on the page, such as images, text, scripts, internal links, and external links.
To measure it, you can use developer tools in the browser or online website analysis tools. For instance, Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox come with built-in developer tools. You can also use:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- WebPageTest
- GTmetrix
- Pingdom
There are two things you need to keep in mind when looking at performance reports: the size of each asset and the number of assets on the page.

The size is measured in kilobytes (KB), and the higher the number, the larger the page. To optimize your site for search engines, you need to keep this number as low as possible and make sure that your site loads quickly and efficiently.
Factors that contribute to a page’s size include:
1. Images
Using images on your website helps capture the attention of your audience and make your page visually appealing. Not to mention, they’re easy to incorporate. Just one Google Image search and you’ll get what you need. However, image size can be the cause of slow response times and high page sizes.
As such, you need to understand image file types, compression techniques, and other strategies for reducing the size of images without sacrificing quality. Fortunately, there are several image optimization practices, but more on that later.
If you want to know the size or weight of your image, you need to look at its pixels. It’s usually measured in bytes, KB, or MB. For instance, if you’re using a Windows system, simply select the photo, right-click, and choose properties. All the information regarding that photo will be shown, including the image dimensions and size.
Additionally, can use tools to check or measure your photo size to ensure you have properly size images like:
- Image Measurement
- Omni Calculator
- Posterburner
To make this easier, you can get a virtual assistant (VA) to help research the tools you can use, look for image optimization services you can hire, or even assist you in applying image compression techniques. This is especially helpful if your regular content includes many images. Plus, a VA can free your schedule to focus on other responsibilities, while they do image searches for your content.
2. Videos
Although video guides are great for making websites interactive, they can also be a major contributor to page size and affect the load speed of the website. These are large files that take a long time to load, which is especially problematic for those who don’t have a good internet connection.
Embedding videos from YouTube is a great way to reduce page size, while still providing an engaging and interactive experience for website visitors. By using YouTube’s embed code, you can easily add videos to your website without having to host them on your server.

A great example of this is a blog post about web design principles. If you look at it, the content has a lot of videos but all are embedded on Youtube. So despite being visual-heavy content the videos won’t have a huge impact on increasing the page size.
3. JavaScript
JavaScript is a pretty amazing tool for building websites. It can do everything from making your website interactive to allowing it to function in any way you want it.
But here’s the catch. It has a bad rap as being “bloated,” meaning it can slow down a website’s load time and eat up more bandwidth.
There are two main reasons why this happens: first, when you use JavaScript code that isn’t optimized for performance (or is written poorly), it will be slower than if it were written well.
The second reason is because of how browsers handle JavaScript files. They load them sequentially instead of loading them all at once (like CSS files), meaning they take longer to download and render on your screen.
4. Custom Fonts
Fonts with too much weight or boldness will have a larger impact on page size than those with lighter weights because they take up more space in pixels than others. This is because custom fonts require additional requests to the server, resulting in slower response times and increased data usage.
As a result, custom fonts increase the file size of your web pages. With a longer load time, you can be sure it’ll lead to poor user experience, which is a big NO for Google Search or other search engines. To ensure better performance and user experience, it’s important to avoid using custom fonts whenever possible.
5. Advertising
Ads are an important source of revenue for many websites, but having too many ads on a page can hurt page size and user experience.
Nowadays, advertisements use high-quality photos, GIFs, or videos, all of which can slow down the loading time of that page, leaving the readers annoyed. Not to mention, it also affects the overall design of the website, making it look cluttered and unprofessional.
Additionally, having too many ads can make it difficult for users to find the content they are looking for. All of these factors can lead to a poor user experience and ultimately hurt the website’s reputation in the long run.
With that, we’ll move to the discussion of website performance, since page size affects it the most.
Why Does Page Size Matter For SEO and Performance?
Page size matters when it comes to SEO because it affects the speed of your site, which in turn affects the speed at which your users can access information. The bigger it is, the longer it takes for your users to download all of its elements (images, videos, etc.) and for their browser to render them into a readable format.
When a user has a good experience on your site, they’re more likely to take action. So if you want an SEO-friendly website that converts well, consider the loading speed.

Slow loading pages makes it difficult for customers to find what they’re looking for. The visibility of content is reduced and customers are unable to find what they are looking for quickly.
In addition to being frustrating for visitors, this can also hurt you in Google’s eyes. So you want to guarantee yours load quickly enough so that people don’t bounce off of them before reading any content.
Bounce rates can help you understand how the users are interacting with your website. It’ll help you identify any issues that may be causing visitors to leave the page quickly. Additionally, it can give you insights into the good and bad pages you have.
Overall, by monitoring the bounce rate, you can make adjustments to your website design and content to improve user engagement and meet the search intent. To help you further, you can do a business assessment. With that, you can gain insights about what you need to do better for greater website performance.
What’s more, having a lower search ranking can have a significant impact on your site’s visibility. Search analytics is a great way to track and analyze your website’s performance and visibility on search engines. For instance, you can use Google Analytics to identify areas to improve or optimize for your website.
What Is The Ideal Page Size For Your Website?
The good news is, there’s no wrong answer. The key to optimizing your page size is balancing three factors: speed, design, and user experience.

In the image above, you can see that the average page weight or size between 2017 to January 2023 has grown significantly. In May 2017, the average page weight was 1376.2 KB for desktop and 1223.7 KB for mobile. Fast forward to February 2023, and the average page weight is now 2324.8 KB for desktop and 2037.3 KB for mobile.
That data gives you a great benchmark of the page size. However, you have to remember that the data is the overall average size of web pages. Some websites are heavier, while others weigh less.
So, when we talk about the ideal page size, we’re saying that the best fit for your site is whatever works best for what you want people to see when they come there. Plus, how they want to interact with your site once they are there should also be considered.
Moreover, your page size would depend on what business you run or what industry you’re in because the type of content you’re producing is likely reliant on that.
For example, if your business is about creating logos, you’ll need to display your work on your website to foster trust and authority. That means plenty of high-res images and graphics on your page. So, you’ll need to apply techniques, such as using vector images, to lower image file sizes to decrease your page size.
In contrast, if your homepage is like Career Sidekick, wherein the content is mostly text, the page size would surely be smaller. If you look at the website, the design is minimalistic with very simple graphics, low-res thumbnails to present their content, and some blog post excerpts.
Following this, it’s time to move on and discuss what you can do to improve your website’s performance without compromising on your content quality.
6 Ways To Reduce Your Website’s Page Size
With the right strategy and methods, you can act on improving the performance of your website and reduce your website’s page size. As such, you can rest easy about not putting your website at risk of being dragged down on search engines.
1. Compress Images
When you’re working on a website, one of the first things you’ll want to do is compress your images. It can help lower the page size and improve the overall performance of your website. Additionally, it helps speed up image delivery, reduces bandwidth costs, and decreases response times.

For now, we’ll discuss image manipulation techniques to help you: lossless and lossy.
The former is an image processing technique used to reduce the size of larger images without losing any detail or information, making them smaller in size while preserving their original resolution. It’s useful for applications like web design and digital photography where it’s important to maintain the highest possible quality of an image.
The latter is another image processing technique that involves removing some of the data from an image to make it smaller in size and easier to store or transfer. The most common type of lossy image processing is JPEG compression, which can significantly reduce the file size of an image while still preserving its visual quality.
You can use many tools for compressing images, including Imagify, which can help you optimize and compress them, even the double-sized images. This tool is especially useful if your content relies heavily on visuals.
For example, a best-of blog post like this guide to podcast software means including many images to demonstrate the products. Imagify can help ensure that your page size is not ballooning by compressing the images without losing quality. That means you’ll still produce top-notch content by clearly displaying the numerous podcast software on the blog.
Another option is to utilize CSS Sprite. It works by combining multiple images into one image, which is then served from the content server. This reduces the number of requests that the browser needs to make to get the content, thus reducing page size and improving page load time.
2. Code Clean-Up
The code size on the page can impact your overall website performance. The more code there is, the longer it takes to load. This is because there’s more work for browsers and servers to do to process everything that needs to be downloaded before they can display anything on the screen.
As such, you must keep your code clean and up-to-date to ensure your website runs smoothly and quickly. You can use performance plugins or tools to help you reduce page size by minifying JavaScript and optimizing CSS files, including:
- WP Rocket
- Closure Compiler
- YUI Compressor
Plus, there’s an excellent guide for developers created by Screaming Frog that discusses universal analytics, content server, link metrics, link types, JavaScript rendering mode, and many more. It’s a great help for those with technical knowledge.
3. Update Your CMS
A content management system (CMS) is the software that powers your website, like WordPress. It’s what allows you to change the text on pages, add new pages, and make other changes to the structure of your site.
Hence, having an up-to-date CMS is essential for optimizing page size and improving user experience. To help you further, you can leverage search analytics data to identify the most important content on a page and reduce the number of unnecessary elements.
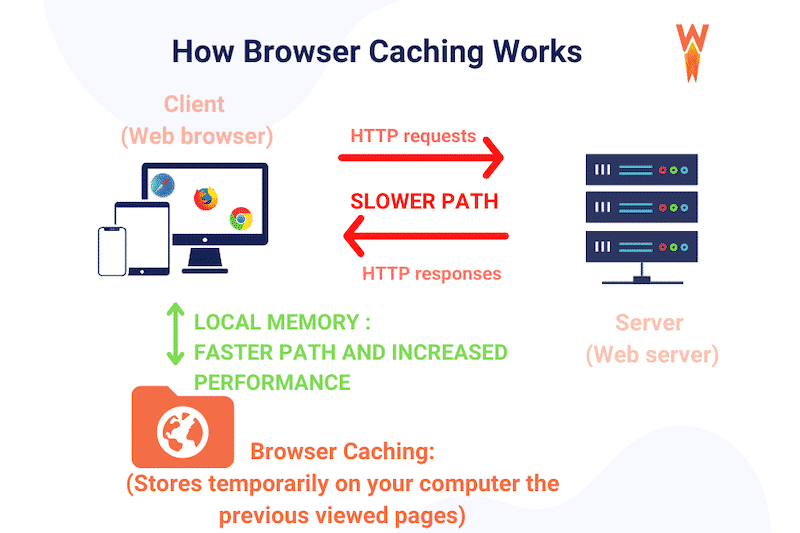
4. Enable Caching
Caching is a way to store frequently-used data so that it doesn’t have to be re-loaded each time you look at the site. This can significantly reduce the amount of processing required to generate a page, which means you can serve more pages per second and less bandwidth is used.

It helps to improve the load speed of your website because it can just load the previously stored version from its cache. Also, caching is great for reducing page size because it means you don’t need to include everything on every page of your site.
There are tools you can use to employ this strategy. For instance, you can use WP Rocket as a WordPress caching performance plugin. You won’t need to worry about the configuration option since it’s easy to install and be activated. And in no time, it can optimize your page thanks to its powerful options, including caching, that are automatically activated right upon activation.
5. GZIP Compression
WP Rocket automatically enables the GZIP compression after activation to reduce the size of your website’s data. This is a process where the size of your website’s data is reduced. It’s a technique used to compress files for faster transmission over the internet. It takes an uncompressed file and reduces its size by removing redundant information, making it easier to download and store.
This helps improve the load speed of your site, as well as reduce your bandwidth usage and page size. That’s because when the server sends your content to the browser, it will compress it before sending it over the wire.
6. Optimize Your Content For Mobile
With all the different types of phones, operating systems, and screen sizes available today, it can be difficult to develop a website that works well across all devices. But companies don’t have a choice because smartphones are the norm. Hence, making your content mobile-friendly is a must.
This means using responsive design techniques to ensure that your content looks good no matter what device it’s being viewed on. Plus, it helps ensure that users have a great experience no matter their device.

This strategy is becoming increasingly important in the world of SEO. Search engines take into account how well a site is optimized for mobile when ranking websites in search results. Just take a look at Google’s stance on the image above. It rewards those who have mobile-optimized content.
A great example of a blog post that needs to be mobile-friendly is this article about the best digital marketing websites. It has a lot of tables to accommodate its 100+ list, and they don’t render well on some smartphones. This could affect user experience and can affect the brand’s mobile SEO.
Wrapping Up
Many factors contribute to the success of SEO, and one of them is the page size. It impacts the overall performance of your website, which in turn affects other elements like user experience. Ultimately, it can be one of the factors on whether your website goes up or down in search rankings. Would page size or website performance be easy to monitor, especially if a website has hundreds of web pages?
Well, that depends. If you have an expert performance optimization service helping you, then the process of analyzing data, optimizing your content, and identifying speed opportunities becomes seamless.
With WP Rocket, the gold standard is what you’ll get. You can integrate it into your WordPress-powered website, and it’ll do the heavy lifting to reduce your website page size and boost performance.
The post Why Page Size Is Important For SEO And Performance appeared first on WP Rocket.





 Important: The next themes are coming with their page builder (or are bundled with Elementor or WP Bakery). That’s why they are in a separate section, and the results are from a new test site with similar elements across the page builders.
Important: The next themes are coming with their page builder (or are bundled with Elementor or WP Bakery). That’s why they are in a separate section, and the results are from a new test site with similar elements across the page builders.




















 It’s a good idea to clear the cache on your WooCommerce site because it prevents you from showing outdated content and products to users.
It’s a good idea to clear the cache on your WooCommerce site because it prevents you from showing outdated content and products to users.











 If you are unfamiliar with caching, we encourage you to read our guide about
If you are unfamiliar with caching, we encourage you to read our guide about